Interesting!!
You only need a cardboard and an Android phone, you could start to develop VR!
Ref: https://www.google.com/get/cardboard/get-cardboard.html
Wednesday, 24 December 2014
Friday, 5 December 2014
J.K. Rowling Speaks at Harvard Commencement
It shows not only her knowledge but also her sense of humor!
Labels:
Success
Wednesday, 5 November 2014
Skin Button
Yeah, I've thought about doing smart phone as a projector, to be a big projector, to show image, slides, video, document... something like that.
BUT! I've never thought about doing it as a tiny projector!
Such a nice idea!
refer: http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2647356
Labels:
Creative
Thursday, 21 August 2014
[C++] Container
| size | add | delete | access | |
| vector | size() | push_back() | pop_back() | [], back() |
| list | size() | push_back() | pop_back() | back() |
| queue | size() | push() | pop() | back() |
| dequeue | size() | push_back(), push_front() |
pop_front(), pop_front() |
[], back() |
| priority_queue | size() | push() | pop() | top() |
| set | size() | iterators | iterators | iterators |
| multiset | size() | iterators | iterators | iterators |
| map | size() | iterators | iterators | [], iterators |
| multimap | size() | iterators | iterators | iterators |
Labels:
CPP
Friday, 1 August 2014
Tuesday, 29 July 2014
[C++] Why we need new/delete in C++? Can't malloc/free do the same thing?
The difference between malloc/free and new/delete is malloc/free are standard library, and new/delete are operator.
Ref.: http://fanqiang.chinaunix.net/a4/b2/20020722/060200273_b.html
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class Obj
{
public :
Obj(void){ cout << "Constructor" << endl; }
~Obj(void){ cout << "Destructor" << endl; }
void Initialize(void){ cout << "Initialization" << endl; }
void Destroy(void){ cout << "Destroy" << endl; }
};
void UseMallocFree(void)
{
Obj *a = (Obj *)malloc(sizeof(Obj));
a->Initialize();
//…
a->Destroy();
free(a);
}
void UseNewDelete(void)
{
Obj *a = new Obj;
//…
delete a;
}
int main()
{
cout << "UseMallocFree" << endl;
UseMallocFree();
cout << endl << "UseNewDelete" << endl;
UseNewDelete();
return 0;
}
UseMallocFree Initialization Destroy UseNewDelete Constructor Destructor
Ref.: http://fanqiang.chinaunix.net/a4/b2/20020722/060200273_b.html
Labels:
CPP
Monday, 28 July 2014
[C++] Constructor/Copy Constructor/Assignment Operator/Destructor
1) Both Copy Constructor and Assignment Operator are call by address, not call by value
the problem caused in this program:
- memory leak in b
- it was copied by "b._array = a._array;", either modified in b or a will change the result
- double free
2) Initialization list
3) Const variable can only be initialed in initialization list
4) The serial of constructor and destructor
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Array {
public:
int *_array;
int size;
Array(int input):size(input)
{
_array = new int[size];
}
void Set(int i, int v)
{
_array[i] = v;
}
int Get(int i)
{
return _array[i];
}
~Array()
{
delete [] _array;
}
};
int main()
{
Array a(5);
Array b = a;
a.Set(0, 10);
a.Set(1, 20);
a.Set(2, 30);
a.Set(3, 40);
a.Set(4, 50);
cout << a.Get(0) << " " << a.Get(1) << " " << a.Get(2) << " " << a.Get(3) << " " << a.Get(4) << endl;
cout << b.Get(0) << " " << b.Get(1) << " " << b.Get(2) << " " << b.Get(3) << " " << b.Get(4) << endl;
cout << &a << " " << a._array << endl;
cout << &b << " " << b._array << endl;
return 0;
}
10 20 30 40 50 10 20 30 40 50 0x7fff61f44a90 0x1180010 0x7fff61f44aa0 0x1180010 *** glibc detected *** ./a.out: double free or corruption (fasttop): 0x0000000001180010 ***
the problem caused in this program:
- memory leak in b
- it was copied by "b._array = a._array;", either modified in b or a will change the result
- double free
2) Initialization list
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A()
{
cout << "A constructor" << endl;
}
A(const A& a)
{
cout << "A copy constructor" << endl;
}
A& operator=(const A& a)
{
cout << "A assignment Operator" << endl;
}
};
class B {
public:
B(A &input)
{
cout << "B consturctor" << endl;
m_a = input;
}
private:
A m_a;
};
class C {
public:
C(A& input):m_a(input)
{
cout << "C constructor" << endl;
}
private:
A m_a;
};
int main()
{
cout << "===A===" << endl;
A a;
cout << "===B===" << endl;
B b(a);
cout << "===C===" << endl;
C c(a);
return 0;
}
===A=== A constructor ===B=== A constructor B consturctor A assignment Operator ===C=== A copy constructor C constructor
3) Const variable can only be initialed in initialization list
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A(int input) { a = input; }
void show() { cout << a << endl; }
private:
const int a;
};
int main()
{
A aa(5);
aa.show();
return 0;
}
test2.cpp: In constructor ‘A::A(int)’: test2.cpp:7:9: error: uninitialized member ‘A::a’ with ‘const’ type ‘const int’ [-fpermissive] test2.cpp:7:28: error: assignment of read-only member ‘A::a’
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A(int input):a(input) { }
void show() { cout << a << endl; }
private:
const int a;
};
int main()
{
A aa(5);
aa.show();
return 0;
}
5
4) The serial of constructor and destructor
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A()
{
cout << "A constructor" << endl;
}
~A()
{
cout << "A destructor" << endl;
}
};
class B {
public:
B()
{
cout << "B constructor" << endl;
}
~B()
{
cout << "B destructor" << endl;
}
};
class C {
public:
C()
{
cout << "C constructor" << endl;
}
~C()
{
cout << "C destructor" << endl;
}
};
class Aa : public A {
public:
Aa(int in1):y(in1)
{
cout << "Aa constructor" << endl;
}
~Aa()
{
cout << "Aa destructor" << endl;
}
private:
B b;
int y;
C c;
};
int main()
{
Aa hi(5);
return 0;
}
A constructor B constructor C constructor Aa constructor Aa destructor C destructor B destructor A destructor
Labels:
CPP
Saturday, 26 July 2014
[C++] The difference between class and struct
class X {
int a; // X::a is private by default
};
struct S {
int a; // S::a is public by default
};
Ref. Working Draft, Standard for Programming Language C++
int a; // X::a is private by default
};
struct S {
int a; // S::a is public by default
};
[note]: the variable in union is also public by default.
Ref. Working Draft, Standard for Programming Language C++
Labels:
CPP
Monday, 14 July 2014
Jeff Bezos delivers graduation speech at Princeton University
"It's harder to be kind than clever."
---
How will you use your gifts? What choices will you make?
Will inertia be your guide, or will you follow your passions?
Will you follow dogma, or will you be original?
Will you choose a life of ease, or a life of service and adventure?
Will you wilt under criticism, or will you follow your convictions?
Will you bluff it out when you're wrong, or you apologize?
Will you guard your heart against rejection, or will you act when you fall in love?
Will you play it safe, or will you be a little bit swashbuckling?
When it's tough, will you give up, or will you be relentless?
Will you be a cynic, or will you be a builder?
Will you be clever at the expense of others, or will you be kind?
Labels:
Success
Wednesday, 25 June 2014
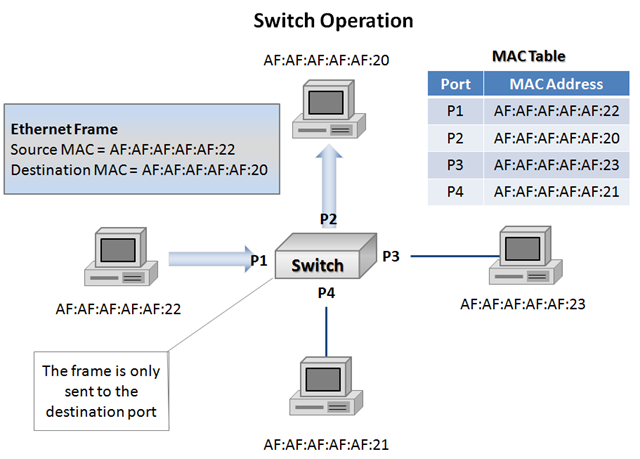
Ethernet Switch
1) Switches are the next evolution of bridges and the operation they perform is still considered bridging. In very basic terms a switch is a high port-count bridge that is able to make decisions on a port-by-port basis.
2) A switch maintains a MAC table and only forwards frames to the appropriate port based on the destination MAC.
3) If the switch has not yet learned the destination MAC it will flood the frame. (I've read some data that says it'll use arp to know the MAC.)
Q: How to collect the MAC Table?
A: Each end-point is labeled with a MAC address starting with AF:AF:AF:AF:AF. The ‘dynamic learning’ is done be recording the source MAC address of incoming frames. While the destination MAC address had not yet been learned, the switch would be forced to flood the frame to all ports except the one it received.
Ref.:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_switch
http://www.definethecloud.net/data-center-101-local-area-network-switching/
Labels:
Network
Bridge
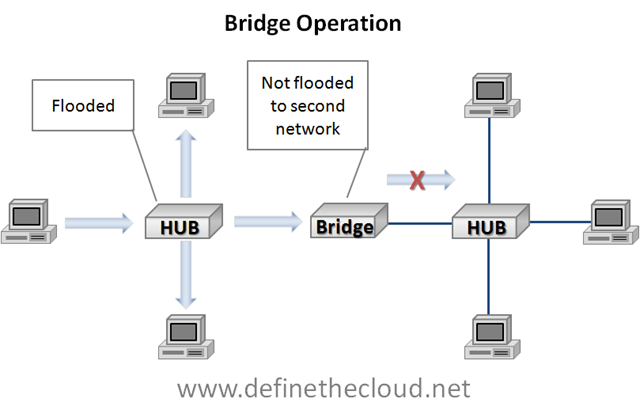
1) A bridge is a device that connects two or more local area networks, or two or more segments of the same network.
2) The original bridges were typically 2 or more ports (low port counts) and could separate MAC addresses using the table for those ports.
3) In the OSI model bridging acts in the first two layers, below the network layer.
Q: How to make a bridge table?
A:
Ref.:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bridging_(networking)
http://www.definethecloud.net/data-center-101-local-area-network-switching/
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc700841.aspx
Labels:
Network
Tuesday, 24 June 2014
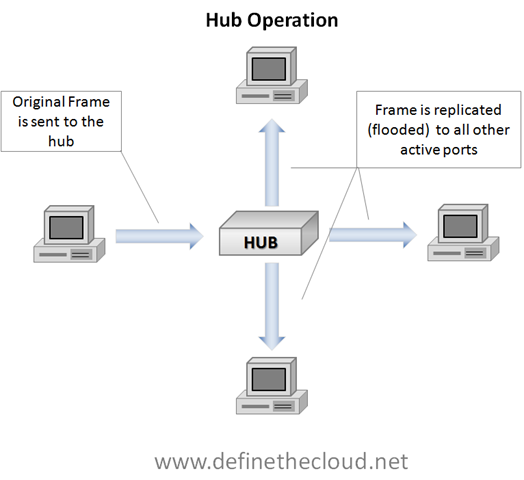
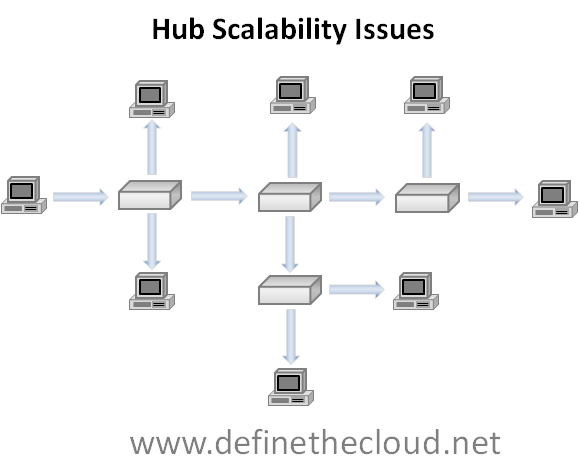
Hub
1) It has multiple input/output (I/O) ports, in which a signal introduced at the input of any port appears at the output of every port except the original incoming.
2) A hub works at the physical layer (layer 1) of the OSI model
3) There's 2 kinds of hub, Passive & Active (which needs adapter & it'll repeat the signals)
Ref.:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethernet_hub
http://www.definethecloud.net/data-center-101-local-area-network-switching/
Labels:
Network
Internetworking
Device
|
PHY
|
Data Link
|
Network
|
Others
|
Repeater
|
Same
|
Same
|
Same
|
Same
|
Hub
|
Same
|
Same
|
Same
|
Same
|
Bridge
|
Same/!Same
|
Same/!Same
|
Same
|
Same
|
L2 Switch
|
Same/!Same
|
Same
|
Same
|
Same
|
Router
|
Same/!Same
|
Same/!Same
|
Same
|
Same
|
L3 Switch
|
Same/!Same
|
Same/!Same
|
Same
|
Same
|
Gateway
|
Same/!Same
|
Same/!Same
|
Same/!Same
|
Same/!Same
|
| OSI Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data unit | Layer | Function | ||
| Host layers | Data | 7. Application | Network process to application | |
| 6. Presentation | Data representation, encryption and decryption, convert machine dependent data to machine independent data | |||
| 5. Session | Interhost communication, managing sessions between applications | |||
| Segments | 4. Transport | Reliable delivery of packets between points on a network. | ||
| Media layers | Packet/ Datagram | 3. Network | Addressing, routing and (not necessarily reliable) delivery of datagrams between points on a network. | |
| Bit/Frame | 2. Data link | A reliable direct point-to-point data connection. | ||
| Bit | 1. Physical | A (not necessarily reliable) direct point-to-point data connection. | ||
Ref.:
http://www.cs.nthu.edu.tw/~nfhuang/chap14.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OSI_model
Labels:
Network
Monday, 23 June 2014
[Motion Sensor] Google Gesture
How touching!
It gets in a different level from Kinect, Leap or Ring.
With the same purpose of self-driving car, considering for minority.
Labels:
Creative
Saturday, 21 June 2014
Music as a Language
There's no bad ideas.
Just like what Victor Wooten said, "if you play C and C# right next to each other, it probably sounds like those notes clash"
"Wrong"
"Bad"
"but if you take the C up in octave, play the C# and C again"
"the sound became beautiful"
"how could the same 2 notes sounds bad, clash in one instance and beautiful in another?"
"take this to life, when we see something bad or awful or horrible in life, maybe we just viewing it in wrong octave"
Change your viewpoint, change your perspective, and there's no bad idea.
Labels:
Success
Elon Musk USC Marshall Undergraduate Commencement Speech
1) Working super hard.
2) Attract great people.
3) Focus on signal over noise.
4) Don't just follow the trend.
5) Now is the time to get risks.
Labels:
Success
Friday, 20 June 2014
Rawlemon Spherical Solar Energy Generator
Rawlemon Spherical Solar Energy Generator
Really impressive!!!
To create fire w/ magnifying glass is what we learned from science class in elementary school.
Somehow, we all forgot to use this simple application.
Rawlemon Solar Devices is on INDIEGOGO.
Labels:
Creative
Thursday, 19 June 2014
Pyro Board
which remind me the music w/ lightening in The Sorcerer's Apprentice
it must full of the burning smell...
Advanced version:
Ref.:
http://nigelstanford.com/Cymatics/
Labels:
Creative
[Motion Sensor] Ring
I've used Kinect to develop a project.
In survey stage, we also consider Leap.
It seems that Ring is also be a good solution.
Labels:
Creative
Nike Football - The Last Game
Playing it like a game, not a job!
And there's no greater danger than playing it safe.
Anyway, it energizes me.
Labels:
Creative
Monday, 2 June 2014
[Standford] Note 1 of Algorithms: Design and Analysis, Part 1
I. INTRODUCTION
II. ASYMPTOTIC ANALYSIS
III. DIVIDE & CONQUER ALGORITHMS
Ref. https://www.coursera.org/course/algo
II. ASYMPTOTIC ANALYSIS
III. DIVIDE & CONQUER ALGORITHMS
Ref. https://www.coursera.org/course/algo
Labels:
Algorithm
Thursday, 29 May 2014
[MIT] Note 2 of Introduction to C and C++
18.01 Single Variable Calculus
Lecture 4 : Data Structures, Debugging
note: Structure Memory
ex.
Ref. http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/mathematics/18-01sc-single-variable-calculus-fall-2010/
Lecture 4 : Data Structures, Debugging
note: Structure Memory
ex.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
struct X
{
short s;
int i;
char c;
};
struct Y
{
int i;
char c;
short s;
};
struct Z
{
int i;
short s;
char c;
};
printf("%ld\n", sizeof(struct X));
printf("%ld\n", sizeof(struct Y));
printf("%ld\n", sizeof(struct Z));
return 0;
}
12 8 8
Ref. http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/mathematics/18-01sc-single-variable-calculus-fall-2010/
Labels:
CPP
[MIT] Note 1 of Introduction to C and C++
MIT 6.S096 Introduction to C and C++
Lecture 1: Compilation Pipeline
Ref. http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-s096-introduction-to-c-and-c-january-iap-2013/
Lecture 1: Compilation Pipeline
Ref. http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-s096-introduction-to-c-and-c-january-iap-2013/
Labels:
CPP
[MIT] Note 1 of Single Variable Calculus
MIT 18.01 Single Variable Calculus
Lecture 1: Compilation Pipeline
Ref. http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/mathematics/18-01sc-single-variable-calculus-fall-2010/
Lecture 1: Compilation Pipeline
Labels:
Math
Monday, 26 May 2014
Unlock Mechanism
It's a cool and creative security solution!
Cant wait to download and try~
Ref. http://www.airsig.com/
Cant wait to download and try~
Ref. http://www.airsig.com/
Labels:
Creative
Wednesday, 21 May 2014
Thursday, 8 May 2014
[C++] Generic Programmin
1) Function templates
2) Class templates
- inherit:
a)
b)
c)
d)
2) Class templates
- inherit:
a)
b)
c)
d)
Ref.: Practice on Programming course from Peking University
Labels:
CPP
Thursday, 1 May 2014
Google Self-Driving Car
Really impressive! It could not only improve road safety and help people who cannot drive.
Labels:
Creative
Monday, 28 April 2014
The Area of Triangle
1. Coordinates

△ABC
= ADEC - △ADB - △BEC
= 1/2(x1y2 + x2y3 + x3y1 - x2y1 - x3y2 - x1y3)
=
2. Heron's Formula
△= sqrt(s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c))
x = 1/2 (a+b+c)
Ref.:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triangle
http://euler.tn.edu.tw/area.pdf

△ABC
= ADEC - △ADB - △BEC
= 1/2(x1y2 + x2y3 + x3y1 - x2y1 - x3y2 - x1y3)
=

2. Heron's Formula
△= sqrt(s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c))
x = 1/2 (a+b+c)
Ref.:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triangle
http://euler.tn.edu.tw/area.pdf
Labels:
Math
Wednesday, 23 April 2014
Systems of Linear Equation in 2 Variable
How many can systems of linear equation have?
1. 1 Solution
2. Infinite Solutions
3. No Solution
C)
If (a1 / a2 == b1 / b2 != c1 / c2), lines are parallel.
-- Situation 3
[Cramer's Rule]


to solve:http://zerojudge.tw/ShowProblem?problemid=a410
Code:
Ref. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cramer%27s_rule
1. 1 Solution
2. Infinite Solutions
3. No Solution
A)
If (a1 / a2 != b1 / b2), it involves lines that intersect exactly 1 time.
-- Situation 1
B)
If (a1 / a2 == b1 / b2 == c1 / c2), it's a same line.
-- Situation 2
C)
If (a1 / a2 == b1 / b2 != c1 / c2), lines are parallel.
-- Situation 3
[Cramer's Rule]
where  is the matrix formed by replacing the ith column of
is the matrix formed by replacing the ith column of  by the column vector
by the column vector  .
.
 is the matrix formed by replacing the ith column of
is the matrix formed by replacing the ith column of  by the column vector
by the column vector  .
.

to solve:http://zerojudge.tw/ShowProblem?problemid=a410
Code:
Ref. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cramer%27s_rule
Labels:
Math
Tuesday, 22 April 2014
[C++] Pointers
Noted down the important concepts:
1. Reference Operator (&)
ex.
ex.
3. Pointers & Arrays
It collects so many ways to get address from an array and set value to an array.
4. Pointers and Const
5. Pointers to Pointers
6. Pointers and Functions
7. Arrow
Same description below:
Ref. http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/pointers/
1. Reference Operator (&)
ex.
myvar = 25; foo = &myvar; bar = myvar;2. Dereference Operator (*)
ex.
baz = *foo;
3. Pointers & Arrays
It collects so many ways to get address from an array and set value to an array.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int numbers[5];
int * p;
p = numbers;
*p = 10;
p++;
*p = 20;
p = &numbers[2];
*p = 30;
p = numbers + 3;
*p = 40;
p = numbers;
*(p+4) = 50;
for (int n=0; n<5; n++)
cout << numbers[n] << ", ";
return 0;
Output:10, 20, 30, 40, 50,
4. Pointers and Const
int x;
int * p1 = &x; // non-const pointer to non-const int
const int * p2 = &x; // non-const pointer to const int
int const * p3 = &x; // also non-const pointer to const int
int * const p4 = &x; // const pointer to non-const int
const int * const p5 = &x; // const pointer to const int
5. Pointers to Pointers
char a; char * b; char ** c; a = 'z'; b = &a; c = &b;
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int addition (int a, int b)
{ return (a+b); }
int subtraction (int a, int b)
{ return (a-b); }
int operation (int x, int y, int (*functocall)(int,int))
{
int g;
g = (*functocall)(x,y);
return (g);
}
int main ()
{
int m,n;
int (*minus)(int,int) = subtraction;
m = operation (7, 5, addition);
n = operation (20, m, minus);
cout << n;
return 0;
}
Output:
8Mostly, we use function point in sqort().
7. Arrow
Same description below:
(*p).foo; p->foo;
Ref. http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/pointers/
Labels:
CPP
Friday, 18 April 2014
Tuesday, 15 April 2014
Thursday, 13 March 2014
Friday, 28 February 2014
Monday, 20 January 2014
Amazon Prime Air
30 min. delivery!
Reminds me the Pizza Hot Motto: 30 Minutes or Free.
Labels:
Creative
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
.gif)
.gif)