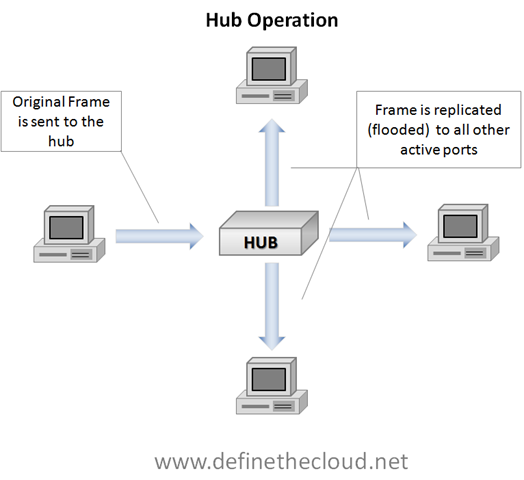
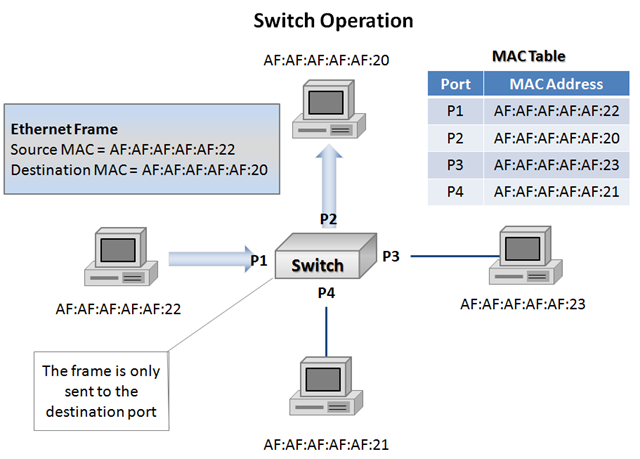
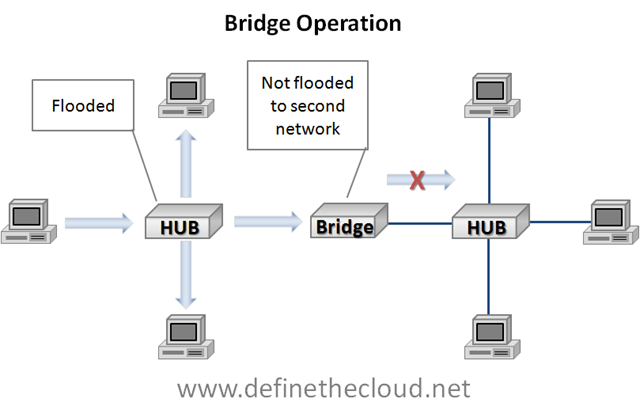
1) Switches are the next evolution of bridges and the operation they perform is still considered bridging. In very basic terms a switch is a high port-count bridge that is able to make decisions on a port-by-port basis.
2) A switch maintains a MAC table and only forwards frames to the appropriate port based on the destination MAC.
3) If the switch has not yet learned the destination MAC it will flood the frame. (I've read some data that says it'll use arp to know the MAC.)
Q: How to collect the MAC Table?
A: Each end-point is labeled with a MAC address starting with AF:AF:AF:AF:AF. The ‘dynamic learning’ is done be recording the source MAC address of incoming frames. While the destination MAC address had not yet been learned, the switch would be forced to flood the frame to all ports except the one it received.
Ref.:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_switch
http://www.definethecloud.net/data-center-101-local-area-network-switching/
.gif)
.gif)